INHERITANCE: (OOP) is when an object or class is based on another object (prototypal inheritance) or class (class-based inheritance), using the same implementation (inheriting from an object or class) specifying implementation to maintain the same behavior (realizing an interface; inheriting behavior). It is a mechanism for code reuse and to allow independent extensions of the original software via public classes and interfaces. The relationships of objects or classes through inheritance give rise to a hierarchy. Inheritance was invented in 1967 for Simula.
There are various types of inheritance, based on paradigm and specific language.
Single Inheritance:
PROGRAM SHOWING SINGLE INHERITANCE:
#include<iostream.h>#include<conio.h>class emp{ public: int eno; char name[20],des[20]; void get() { cout<<"Enter the employee number:"; cin>>eno; cout<<"Enter the employee name:"; cin>>name; cout<<"Enter the designation:"; cin>>des; }};
class salary:public emp{ float bp,hra,da,pf,np; public: void get1() { cout<<"Enter the basic pay:"; cin>>bp; cout<<"Enter the Humen Resource Allowance:"; cin>>hra; cout<<"Enter the Dearness Allowance :"; cin>>da; cout<<"Enter the Profitablity Fund:"; cin>>pf; } void calculate() { np=bp+hra+da-pf; } void display() { cout<<eno<<"\t"<<name<<"\t"<<des<<"\t"<<bp<<"\t"<<hra<<"\t"<<da<<"\t"<<pf<<"\t"<<np<<"\n"; }};void main(){ int i,n; char ch; salary s[10]; clrscr(); cout<<"Enter the number of employee:"; cin>>n; for(i=0;i<n;i++) { s[i].get(); s[i].get1(); s[i].calculate(); } cout<<"\ne_no \t e_name\t des \t bp \t hra \t da \t pf \t np \n"; for(i=0;i<n;i++) { s[i].display(); } getch();}Output:
Enter the Number of employee:1
Enter the employee No: 150
Enter the employee Name: ram
Enter the designation: Manager
Enter the basic pay: 5000
Enter the HR allowance: 1000
Enter the Dearness allowance: 500
Enter the profitability Fund: 300
Multiple Inheritance:
#include<iostream>using namespace std;class A{public: A() { cout << "A's constructor called" << endl; }};class B{public: B() { cout << "B's constructor called" << endl; }};class C: public B, public A // Note the order{public: C() { cout << "C's constructor called" << endl; }};int main(){ C c; return 0;}
Output:
B's constructor called
A's constructor called
C's constructor called
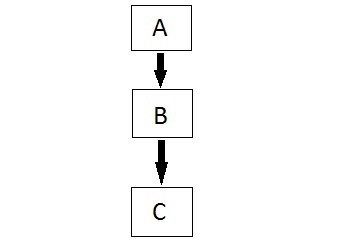
Multilevel Inheritance:
In this type of inheritance the derived class inherits from a class, which in turn inherits from some other class. The Super class for one, is sub class for the other.
PROGRAM SHOWING MULTILEVEL INHERITANCE:
Output:
Base class content.
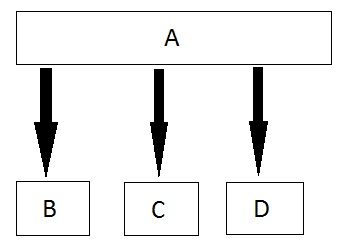
Hierarchical Inheritance
In this type of inheritance, multiple derived classes inherits from a single base class.
Program showing hierarchical inheritance:
#include <iostream.h> class Side
{ protected: int l; public: void set_values (int x) { l=x;} }; class Square: public Side { public: int sq() { return (l *l); } }; class Cube:public Side { public: int cub() { return (l *l*l); } }; int main () { Square s; s.set_values (10); cout << "The square value is::" << s.sq() << endl; Cube c; c.set_values (20); cout << "The cube value is::" << c.cub() << endl; return 0; } OUTPUT:
The square value is:: 100
The cube value is::8000 Hybrid (Virtual) Inheritance
Hybrid Inheritance is combination of Hierarchical and Multilevel Inheritance.
Program showing Hybrid(Virtual) Inheritance#include<iostream.h>#include<conio.h>class A //Base class{public:int l;void len(){cout<<"\n\nLenght :::\t"; cin>>l; //Lenght is enter by user }};class B :public A //Inherits property of class A {public:int b,c;void l_into_b() {len();cout<<"\n\nBreadth :::\t";cin>>b; //Breadth is enter by user c=b*l; //c stores value of lenght * Breadth i.e. (l*b) . }};class C{public:int h;void height(){cout<<"\n\nHeight :::\t";cin>>h; //Height is enter by user }};//Hybrid Inheritance Levelclass D:public B,public C{public:int res;void result(){l_into_b();height();res=h*c; //res stores value of c*h where c=l*b and h is height which is enter by user cout<<"\n\nResult (l*b*h) :::\t"<<res;}};int main(){clrscr();D d1;d1.result();getch();}
|





No comments:
Post a Comment